FODMAP Diet: What It Is And What Are The Benefits

Have you ever heard of the FODMAP diet? Do you suffer from problems related to the large intestine, such as gas, abdominal pain, bloating or diarrhea? So keep reading because this diet could be the solution to your problems.
What is the FODMAP diet?
The term FODMAP is an abbreviation for “oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and fermentable polyphenols”. This means that you will eliminate short-fermented high-carbohydrate vegetables from your diet.
Even though some people may have them among their favourites, not all organisms have the ability to synthesize them well. This diet is especially perfect for anyone who has problems with:
- Crohn’s disease.
- Ulcerative colitis.
- Irritable colon.
Unlike a large number of extreme diets that seek to lose weight indiscriminately and in record time, without paying attention to health, this diet is very well thought out and developed.
Furthermore, it is not intended to make you lose pounds, but to avoid short-term and long-term discomfort.
What foods should we avoid on the FODMAP diet?
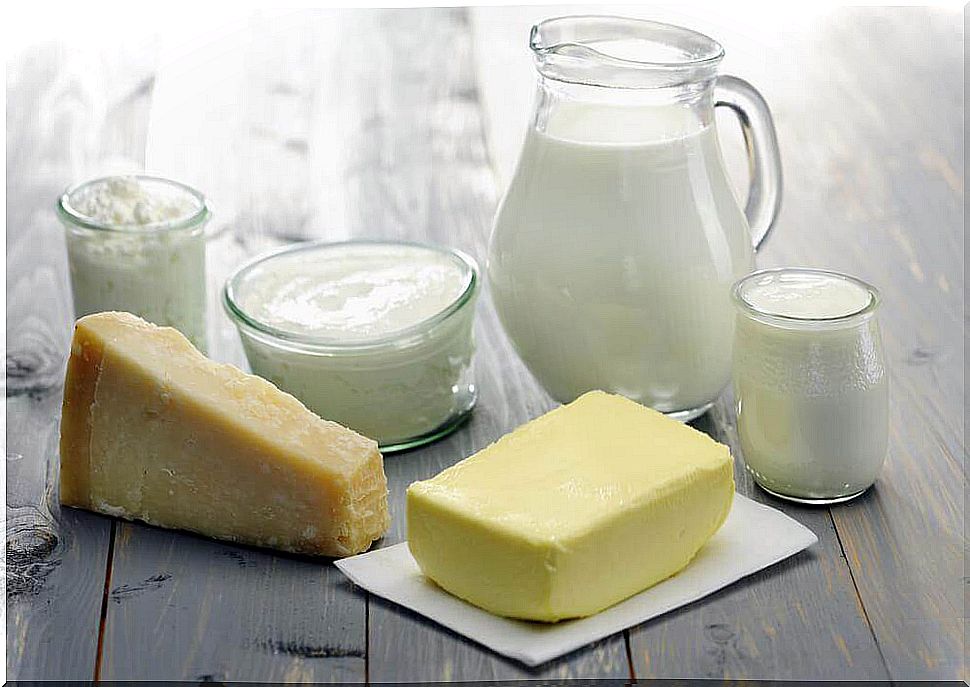

These are foods with some of the FODMAP characteristics and therefore you should avoid:
- Foods rich in galactooligosaccharides: legumes.
- Foods rich in fructooligosaccharides: garlic, rye, wheat and onions.
- Products rich in sorbitol, xylitol and mannitol: sweeteners and light products .
- Natural sweeteners for containing fructose: syrups, honey, jellies.
- Foods with lactose: milk and its derivatives.
Benefits of the FODMAP Diet
Be aware that, at first glance, the FODMAP diet seems very restrictive. However, and before you ignore it, we want you to know the benefits gained from following it.
1. Reduces irritable bowel syndrome symptoms by up to 76%

A large number of people who follow this diet can forget about gas, bloating and stomach pain, as stated in a study published in the journal Nutrients .
In this sense, it is important to consider that many of the foods that this diet does not recommend ferment in the intestine. Therefore, we must be sensible when choosing and opting for foods rich in fiber that promote intestinal transit.
For example, you can eat homemade brown rice or quinoa preparations instead of commercial brown bread.
2. Discomfort reduction in patients with Crohn’s disease
The FODMAP diet positively alters the quantity and quality of prebiotics.
If you don’t want to follow this diet for life because it’s too restrictive, you can try implementing it for a few weeks and then incorporating the foods gradually and without excess. You can repeat the process once a month to give your body a rest.
Just remember to be constant. The fact that you control or avoid a food group one day does not imply that you will be able to eat it indiscriminately afterwards, as the effect can be even more painful.
3. Reduces symptoms of chronic fatigue
No matter how much you eat, do you always feel tired? The FODMAP diet has been proven to help reduce this fatigue. The body will no longer receive foods that make it expend more energy than it gets, especially if we talk about sweeteners.
Remember that the best sugar is the one that comes from the whole fruit. This is due to the fact that it is accompanied by fiber, which reduces glucose peaks and fermentation.
Foods allowed in the FODMAP diet

Not everything is a restriction on the FODMAP diet. Some of the foods that can be eaten are:
- Natural oils.
- Natural sweeteners.
- Natural herbs, condiments and spices.
- Natural nuts and seeds free of preservatives and sweeteners.
- Whole grains: corn, oats, brown rice, quinoa, sorghum and natural tapioca.
- Any meat and its derivatives, provided it is free of fructose and sweeteners.
- Complete fruits, not just juice: bananas, blackberries, oranges, kiwis, strawberries, melon, tamarind and lemon.
Remember that not all diets are aimed at losing weight. Some simply seek to help lead a healthier life free from physical pain and discomfort.