Diet For Athletes With Diabetes

Exercise is essential for people with diabetes, as it has been shown that regular physical activity is related to improved glycemic control, as well as greater weight control. If you suffer from diabetes and already practice or are thinking about starting to play sports, find out below what the diet of athletes with diabetes should be.
What should the diet of athletes with diabetes be like?
The recommended diet for a person with diabetes should be similar to that of a healthy person, as there is no specific ideal percentage of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. The key with diabetes is to eat a variety of healthy foods from all groups.
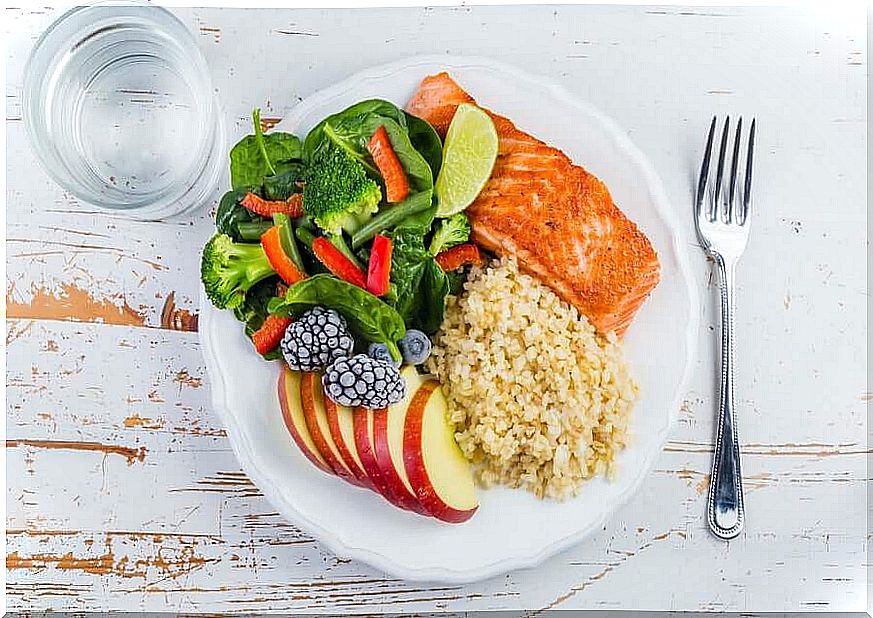
To do this, we can count on the Harvard dish:
- Half of the dish should contain vegetables, both raw and cooked.
- A quarter of the dish must be composed of proteins of animal or vegetable origin, such as meat, white and fatty fish, eggs, dairy products and legumes.
- The other quarter of the dish should be whole grains or tubers.

General recommendations for athletes with diabetes
When practicing any type of sport, a series of recommendations adapted to your situation should be taken into account, as well as the duration and intensity of the exercise you will perform:
- It is necessary to control and monitor blood glucose before, during and at the end of exercise to avoid severe blood glucose changes, according to an article published in Medicine and Sport Science . This check should be more frequent if it was recently started. Depending on the blood glucose level:
- Less than 70 mg/dl: exercises are not recommended.
- Between 70-99 mg / dl : it is recommended to eat in advance.
- Blood glucose between 100-250 mg / dl : you can exercise without eating.
- Above 250 mg / dl: do not exercise and measure ketone bodies.
- In people who take insulin or secretagogues, exercise can cause hypoglycaemia if the drug dose or carbohydrate intake is not changed.
- Always carry the ‘diabetic kit’, which consists of high glycemic index carbohydrates (glucose gels, juices, sports drinks…), a glucose meter and an insulin pen.
- Adequate hydration must be maintained, with water as the main beverage.
How much carbohydrate should I eat?
In the diet of athletes with diabetes, it is important to control the amount of carbohydrates ingested because, in sports, our glucose reserves are depleted.
The type of physical exercise you perform also influences, as in very short or low intensity exercises this does not usually happen, while in activities longer than 45-60 minutes or medium or high intensity the reserves are depleted more quickly.
When exercise exceeds 45-60 minutes or is of medium or high intensity, the daily amount of carbohydrate you should eat is as follows:
- If 3-5 weekly sessions of 1 hour are performed : 4-5 g HCO/kg body weight.
- More than 5 weekly 1 hour sessions: 5-6 g HCO/kg bodyweight.
- More than 5 weekly 2-hour sessions : 7-8 g HCO/kg bodyweight.
- More than 5 weekly sessions of more than 2 hours: 8-10 g HCO/kg bodyweight.

What should I eat before exercising?
The pre-workout meal should include carbohydrate-rich foods along with some protein foods. Whole milk with cereal or a turkey and cheese sandwich are two examples. It is advisable to choose foods that are easily digested, avoiding those that are fatty or very high in fiber.
It is advisable that this meal be taken 2-3 hours before the beginning of the exercise, or 1-2 hours before the activity is done in the morning or in the case of diabetic athletes who use insulin.
You can also include a sports supplement that has been shown to increase the rate of fat oxidation, such as caffeine.
Should I eat while exercising?
During exercise, nutrition will be important depending on the type and duration of the activity.
- If exercise lasts less than 30 minutes, you may not need to eat anything.
- The higher the exercise intensity, the more glucose and fat are consumed ; therefore, it is advisable to consume carbohydrates such as juices, dried fruits, cereal bars or gels.
And as soon as the exercise ends?
After exercise, you must ensure the replacement of carbohydrates, especially those with low glycemic index, such as fruits and oilseeds.
In case of hypoglycemia, it is recommended to follow the 15 × 15 rule. Eat a food that provides 15g of fast-absorbing carbohydrates (one and a half envelopes of sugar, a glass of juice, or a sports drink) and wait 15 minutes for your blood glucose levels to recover. It is also important to include protein in the diet, as has been shown, along with carbohydrates to restore glycogen.
It is important to remember that these are general recommendations. If you are a diabetic athlete, don’t hesitate to look for a professional to customize your diet and workout. If you have any questions, consult your doctor.