The Baobab Fruit: Characteristics, Benefits And Contraindications
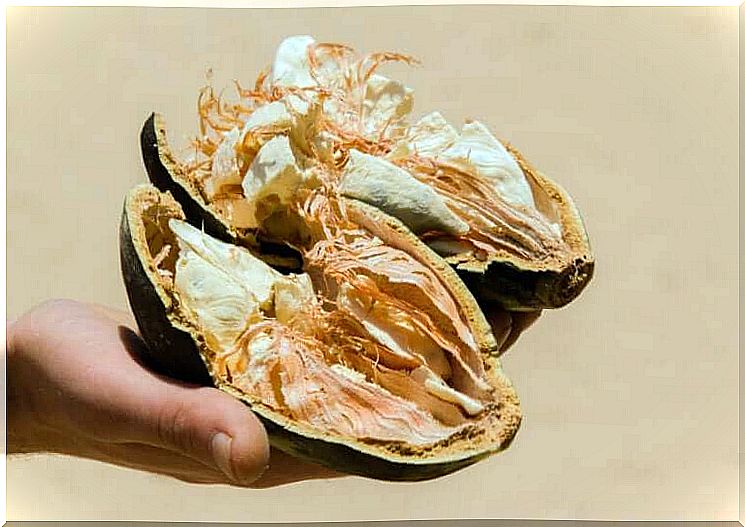

From relieving a toothache, fever or even a pesticide, the baobab berry has more than 300 traditional uses in different parts of Africa. However, perhaps the most relevant is the one that made it the main source of food in that region. Of its 8 species, the best known is Andasonia digitata , whose fruit is considered a superfood.
This gigantic tree is part of ancient legends that describe it. It is said that because she was so vain, God hung her upside down, with the branches on the ground and the roots on top. Its name has Arabic origins and means ‘father of many seeds’.
The baobab fruit is found inside a hard oval pod, in which the pulp containing the bittersweet seeds is stored. A group of experts considers its nutrient richness to be remarkable.
It is marketed as a powdered food that crosses borders. However, as it is new in some countries, some risks are still being studied. Read on to learn more about this interesting fruit, its benefits and contraindications.
Nutritional properties of baobab fruit
A study refers to the baobab fruit as a “superfruit” because, in its nutritional profile, some nutrients such as vitamins, minerals and fatty acids stand out in a high proportion.
Baobab fruit is very rich in vitamin C and fiber. According to a group of pharmacists, fruit pulp contains between 7 to 10 times more vitamin C than oranges, with values ranging from 280 to 300 milligrams per 100 grams of fruit.
With the consumption of just 40 grams of baobab pulp, it is possible to cover 100% of the daily intake of vitamin C recommended for pregnant women. The vitamin B1 and B6 content also stands out. Regarding minerals, calcium values vary between 250 and 350 milligrams per 100 grams of pulp.
Potassium is also abundant in baobab fruit: between 1240 and 1578 milligrams, which is 4 times greater than in bananas. The magnesium content is 5 times higher than that of avocado.
Other studies highlight that 36% of the nutrients are carbohydrates, such as glucose, fructose and sucrose, which give the seed a sweet taste. Another part is the soluble fiber, represented by pectin. As if that wasn’t enough, the high concentration of essential fatty acids in the baobab fruit, such as omega 6 and omega 9 was also studied.
Despite its nutritional properties, most experts agree that more studies are needed on the bioavailability of nutrients from the baobab fruit and its products, since there is little information about it.
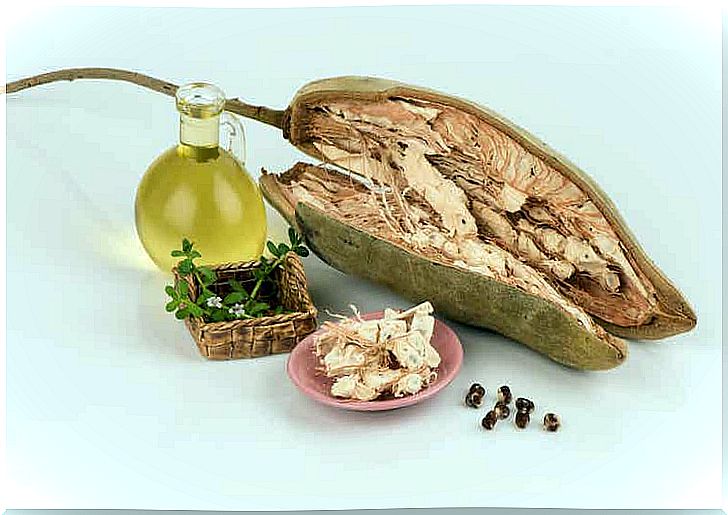

Possible Benefits of Baobab Fruit
The presence of a high concentration of nutrients and other active phytochemicals in the baobab fruit is related to several health benefits, which we will comment on below:
- For the skin: several researchers recognize that the oil from the baobab fruit participates in skin cell renewal due to the presence of vitamin A. Vitamin E participates as an antioxidant.
- Regulates blood pressure: high potassium content has a vasodilating effect. In this way, the risk of pulmonary embolism and heart disease is reduced.
- Strengthens the immune system: the high content of vitamin C allows you to increase levels of white blood cells.
- It can support bones: the high content of calcium and magnesium promotes bone health. It is indicated in diets for the prevention of osteoporosis.
- Analgesic and anti-inflammatory: a possible analgesic and antipyretic effect of the warm extract of the baobab fruit was tested. A study demonstrated the anti-inflammatory activity of the pulp in laboratory animals.
- Antioxidant: the high phenolic content of the fruit stands out for its antioxidant capacity. Some authors have suggested its use as a food supplement.
- Hepatoprotective: The results of a study suggest that consumption of the fruit could have a protective effect on the liver of laboratory animals, due to triterpenoid compounds and sterols.
- Gastrointestinal health: Baobab fruit is used on the African continent to relieve constipation, gastroenteritis and diarrhea. The presence of soluble fiber can stimulate the growth of beneficial bacteria in the intestine.
How can it be ingested?
The baobab fruit is considered a staple food in many regions of Central Africa. The pulp is dissolved in water or milk to be used as a drink and sauce. Furthermore, it is used as a fermenting agent in local brewing and is a good substitute for cream of tartar in baking.
The pulp can also be used to make ice cream, juices and jellies. It must never be cooked and is added at the end, when the recipe is already at room temperature.
Seeds can be eaten fresh or dried, ground into flour to add to soups, and stewed as a thickener. They can also be roasted before being crushed into a paste; then they will be fermented and dried.
The commercial presentation for sale is in powder form, which can be used as a sports supplement as well as in nutritional formulations. It can be incorporated into smoothies, cereals, cereal bars, yogurts, dairy products and juices.

Is there any risk in your consumption?
Although the baobab fruit has been certified safe in the United States and the European Commission has authorized its importation as a novel food, tests on its healthy properties have been carried out only on animals.
Therefore, until research is carried out on the risks to humans, it should be consumed with caution, respecting the recommended portions. There are many nutritional, medicinal and health benefits it provides, but we must be careful with excessive consumption.